The electronic signature market has existed for more than 20 years, but its most significant expansion and adoption was over the past 10 years. The advent and proliferation of mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets and touchscreen computers has led a higher need for electronic signatures in optimizing business processes and eliminating paper-based work. We at FPT have developed an Electronic Signature solution to simplify the signing process and provide clients with an easy-to-use application for improving efficiency within their business.
History of e-Signature
In today’s hustle and bustle business context, the demand for speeding up work processes to optimize efficiency while still ensuring data security has become more pressing and necessary than ever. The use of electronic signatures continues to evolve as a means to verify documents, and attain faster and safer authentication methods that cannot be easily compromised.
(Related: The Four Big Challenges to Data Management in HealthCare)
Let’s review how important and confidential documents were signed in the past. First, a user would retrieve the documents to be signed through mail or print the document from the designated online source. Documents were directly sent to signers for handwritten signature and then returned to the person who created or stored the data. The signing process cost lots of time and money, as when signed documents were returned, additional steps were needed to verify the signature. Nowadays, with the development and widespread use of e-Signature, users may securely access, view and sign online documents, and remove most of the time-consuming procedural steps.
E-Signature, also called electronic signature, is responsible for identifying the person who has signed the document for contractual purposes and is equivalent to a wet signature. It can be in the format of a scanned image, a verbal confirmation or a tick that can be used on an electronic document. For example, when you sign your name on a courier’s mobile device, that’s an electronic signature.
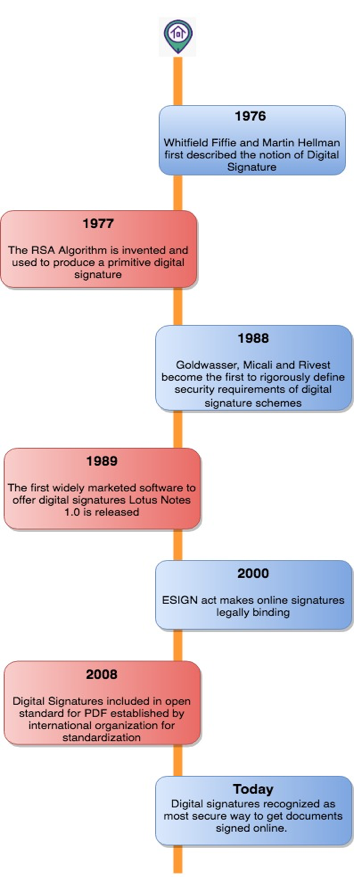
Figure 1: The Evolution and History (Source)
In fact, people have been using contracts with electronic signatures for more than 100 years but in the form of Morse code and telegrams. In the 1970s, businesses and individuals began using fax machines to transmit important documents. Although the signatures on these documents are still displayed on paper, the process of transmitting and receiving them is based entirely on electronic signals, so they are considered electronic signatures. Currently, with the development of innovative technologies, electronic signatures are becoming more widely used.
The Importance of e-Signature
A number of factors have been driving many highly-regulated industries to the adoption of electronic signatures on digital paperless documents. The industries are quite diverse, such as financial services, education, mortgage, insurance, government, healthcare, small businesses and even crowdfunding.
What’s driven that change?
- Increased Speed
There are several ways e-Signature brings greater speed than the tradition wet-based signing. Document delivery occurs sooner. Signing appointments and processing times are reduced through the use of e-Signature. Time spent on manual paper-based procedures is significantly reduced and can securely complete the approvals and agreements in hours rather than days.
- Convenience
E-Signature has an opportunity to really change the user experience. Users are allowed to review documents in advance and ask questions to the appropriate parties before signing from any location.
- Enhanced Security
The e-Signature feature provides a higher level of security in many applications by securely storing sensitive business data. It also quickly identifies any document alterations and controls who has access to private information. Many businesses are adopting the technological solutions of e-Signature.
- Improved Quality
E-Signature eliminates manual operations and improves accuracy and consistency of the documents by automating data validation. This ensures that sections requiring a signature are signed.
Major Global Players
Significant investments have been made into the e-Signature market as more Electronic Signature Apps have been introduced to service business’ needs.
Figure 2: Best Electronic Signature Apps
E-Signature software allows easy collection and storage of these types of signatures and also increases security by ensuring that signatures are verified.
(Related: Why Most of Digital Transformations Will Fail Without OCR?)
Mortgage in US market and Challenges with Signing
The US real estate market is an international market, as it attracts investors from all over the world. According to the American Real Estate Broker Association, in 2017, foreigners spent $153 billion to buy more than 284,000 homes in the US and Vietnamese citizens are ranked 7th in the list. The attraction of American real estate is largely due to the quick trading process. Property titles (Red books) are granted quickly and inexpensively. The owner can buy and sell easily, and usually within 2 weeks the deed is recorded. This optimization is because the closing process has been significantly reduced at the signing phase.
In the past, at closing, the parties involved in the real estate sale had to review a variety of documents related to the mortgage loan and the sale of the home (Property deed, Bill of sale, Transfer tax declaration, Mortgage agreement and note, Closing Disclosure form) before signing. Reviewing and signing documents in real estate took a lot of time and passed through many parties. Even though signers have right to read and understand the documents, many errors were still found after closing.
When the use of e-Signature was leveraged in the closing process, the paperwork review process has been reduced, signing has become much easier and has overcome many oversight mistakes. Closing documents can be sent to the signer via email before the closing date. Signers have more time to review the documents at their own pace, read the whole document carefully and directly input their signature into the document.
In 2000, Congress passed the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (ESIGN), which broadly established the legal equivalence of electronic and handwritten signature. 15 years later, FHA (Federal Housing Administration) announced the acceptance of electronic signature on a much broader set of mortgage and closing documents than ever before. Therefore, many e-Signature platforms have become widely utilized and leveraged across many industries.
FPT has experience in the Mortgage and Title Insurance industries for more than ten years with a variety of mortgage-related projects, many of which provide solutions for the closing process. In compliance with the US e-Sign regulations and policies, developing an e-Sign solution to improve the user experience when signing documents has become a priority.
E-Signature in Vietnam
In Vietnam, e-Signature has begun to be used in e-commerce transactions and is also commonly found in legal agencies. The popularity of Internet-based transactions between businesses, individuals and governments has become common and more widely practiced. Previously, we were accustomed to solutions such as electronic bills, e-tax payment, etc. But recently, the use of electronic signatures is a more comprehensive solution, solving a lot of problems, saving time and money for businesses and bringing a higher level of efficiency.
The e-Signature technology is growing rapidly worldwide, but in Vietnam, it is commonly used in only two main industries: Banking and Accounting. In the near future, it is possible that the electronic signature will become more popular both in business and individual users. Therefore, it is important to choose the most effective and secure e-Signature services, so that electronic signatures become more popular and bring the country closer to paper-less signing.
On September 27, 2018, the VietNam Government issued Decree No. 130/2018/ND-CP provided details of the implementation of the Electronic Transaction Law on Digital Signature and Digital Certification services. This Decree came into effect from November 15, 2018, creating a strict but simple legal framework that helps organizations and individuals in using electronic signatures, digital signatures and digital certificates in electronic transactions.
(Related: CIFAR10: 94% Of Accuracy By 50 Epochs With End-to-End Training)
E-Signature Solution Description
Currently almost all business processes that require signatures is still paper-based with a limited amount of technological intervention. An e-Signature development should be a major step toward implementing technology solutions. The customer may send documents in PDF form to all stakeholders with only one click, and each of them will receive an email to access the signing page and perform the e-Signature(s). The duration of signing and documents transfer is shortened from weeks to days or even minutes, while eliminating the need for express services.
After all stakeholders have completed the signing process, the documents with e-Signatures are digitally tamper-sealed for protection and integrity. Any changes to the seal indicate that the document has been compromised. The process of tamper-sealed evidence or digital signature is described below:
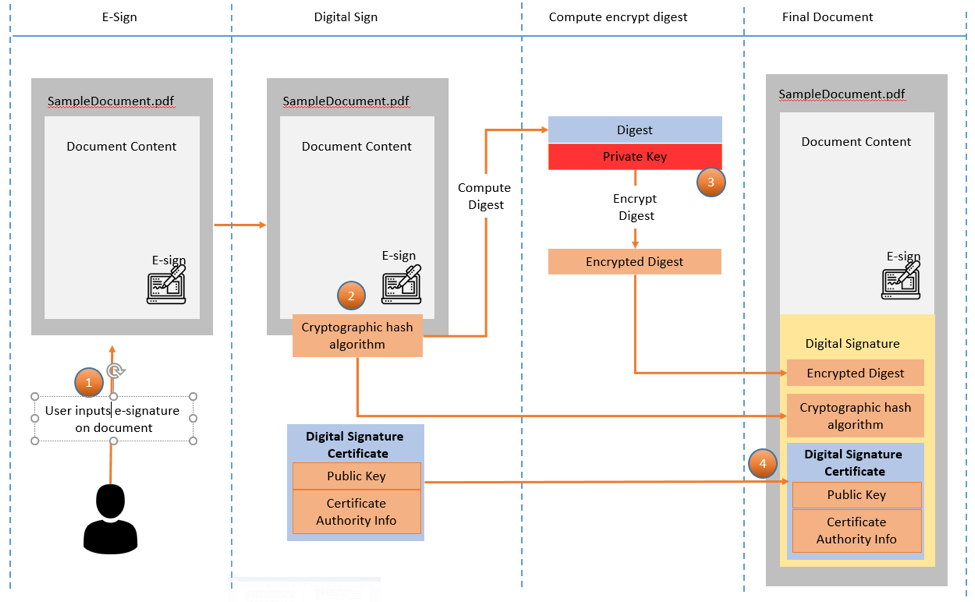
In compliance with regulations, the e-Signature solution must use a server system and HSM (Hardware security modules) with highest security standard along with a number of open-source products to implement complex cryptographic algorithms. First and foremost, the signer will need a pair of public key/private key and a Digital Certificate to prove the ownership of the Public Key. A Digital Certificate is also known as a Public Key Certificate or Identity Certificate. Digital certificates for an entity contain the following information:
- Subject: the name of the person or entity being certified including: Tax number, Name of the Company
- Serial Number: a serial number of digital certificate
- Valid From: the date from which the certificate is valid
- Valid To: the expiration date of the certificate
- Issuer: the name of the CA that issued the certificate (e.g: VNPT- CA)
- Signature: the actual digital signature of CA that issued the certificate
- Basic constraints: things related to the responsibilities of CA
- And other required elements based on regulations in each country
Afterwards, the following steps are taken to complete the process:
- Compute a digest of the content of the document (for example: SHA-256 Hash Algorithm).
- Encrypt the Hash Value from step 1 using the private key.
- Create a digital signature that includes the following components:
- Encrypted result from step 2
- The hash algorithm used
- Public key
- Digital Certificate to prove that you have signed the document
- Insert signature into document.
- Once the signature has been added into the document, the final version of the document will be forwarded to the relevant parties for verification.
- After receiving the document, the verifier will need to run through a number of algorithms to re-examine the validity of Digital Certificate and Digital Signature. Even though this is a complex mechanism, it has been integrated into many reading tools such as Foxit, Adobe Reader and Microsoft Office. The software will generate warning message if there is any problem with signatures such as the Certificate has expired, the Account has been repaired or the digital signature was changed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Electronic Signature has become a global commodity. This has had a positive impact on many industries worldwide. As far as a software solution for Electronic Signature is concerned, FPT’s e-Signature solution is an innovative application of information technology that has enormous potential for business operations. The tremendous importance of Electronic Signature in Banking and Government industries has been examined and the solution offers many promising changes; Changes that radically alter customer expectations about the complexity of the closing paperwork process.
References
- https://www.cygnature.io/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/Digital-Signature_Overview.pdf
- https://blog.hubspot.com/sales/electronic-signature
- https://www.firstam.com/assets/eclosing/img/band-types-infographic-graphic-1.jpg
- https://www.itbusinessedge.com/slideshows/six-e-signature-security-requirements-for-digital-transactions-05.html
- https://www.signnow.com/uploads/SignNow_Legality_of_eSignatures_white_paper.pdf
- https://www.signix.com/blog/bid/108804/infographic-the-history-of-digital-signature-technology
- https://knowledge.digicert.com/solution/SO4583.html
- https://cer.vn/news/kien-thuc/cac-phien-ban-cua-chung-chi-so-x-509/