Blockchain technology, not long ago, has been a breath of fresh air in the 4.0 industrial revolution and gained considerable attention from people in the tech world in general and researchers in particular. From a technical perspective, this is mainly due to its exclusive features, including decentralization, immutability, security and traceability. Derived from those technical features, many applications of blockchain have been brought to life and solved a lot of problems in many areas such as finance, commerce, supply chain management and healthcare.
Even though an increasing number of blockchain-based applications have been developed for educational purposes, only a few of them were put into use. For that reason, there’s still a big question mark over its potential in this field in the future.
In this article, I focus on discussing three key concepts, including the current educational problem description, the potential use of blockchain in education and Smart Certificate.
Degree Fraud Problem
Certificates play a critical role in both education and resources management. Individual learning records become essential for people’s career development. These educational items, therefore, should be stored in a ledger which exists permanently and cannot be tampered with.
Over the last few decades, there were numerous cases of degree fraud. With the fast-paced development of technology, it has never been easier to fake a professional-looking degree certificate or to gain one on the internet. According to The New York Times (2015), there are 3.300 unidentified institutions of higher education worldwide selling degrees to anyone willing to pay, and more than 50,000 Ph.D.s are purchased from diploma mills annually [1]. Besides, a survey conducted by CareerBuilder.com (2014) indicated that 58% of nearly 2,200 HR managers had caught lies on the resumes and one of the most common lies which accounts for approximately 33% per cent related to the academic degree [2].
In response to the problem, many solutions have been found to reduce the degree fraud. However, none of those has been able to solve this issue thoroughly so far.
Read more: Health Insurance Claim: Machine Learning for Fraud Detection
Why Use Blockchain Technology
Based on the above mentioned four features, some benefits of Smart certificate – an educational application using blockchain technology are described as below:
1. Help the employer reduce costs and time of traditional verification of certificate by providing proof of achievement and membership.
2. Help the institution save time and money for producing certificate papers.
3. Provide lifelong storage.
4. Protect the certificate from mutation.
5. Help Informal learning like online learning, boot camps becomes more secure, trustable and recognized, which is recently unappreciated and short of official certificates.
6. Students take full of responsibility to protect and share their certificates without the need of a central party.
Nowadays, some universities have adopted blockchain technology to manage and verify academic degrees. For examples, the University College London in the UK and the University of Nicosia in Cyprus use Bitcoin blockchain for verification of academic qualifications [3][4]. MIT Media Lab built a digital academic certificates system on the Bitcoin Blockchain [5]. An applicable educational infrastructure is developed by Sony Global Education for Open Sharing of Academic Proficiency and Progress Records [6].
Related: Digital ID in Supply-chain: Mutual Understanding among Suppliers
Blockchain-Base Solution – Smart Certificate
The following solution below is making use of the Ethereum Smart Contract. According to Imran Bashir (2017), Smart Contracts are automated, autonomous programs that run on the blockchain and contain logic and code in order to execute a required function when certain conditions are fulfilled [7].
*Note: The primary purpose of this article is to give you an idea of how we can apply blockchain to solve an educational challenge, not to instruct you in programming a Smart Contract or developing a Decentralized Application professionally.
With the emergence of blockchain technology, degree fraud is no longer a fear for education and resources management. Blockchain provides a practical solution for issuing, validating and sharing certificate without the concern about its integrity. The idea is to create two different contracts named Factory and Certificate. While the first one is responsible for examining the standard of the issuer in order to eliminate unrecognized universities, schools and institutions, the second takes charge of containing information about the certificate and the owner.
Setting up rules for the Factory contract:
- Only the Factory creator can add qualified issuers to the list.
- Only the issuers included in the list can create certificates.
- Only the Factory creator can remove issuers from the list.
Setting up rules for the Certificate contract:
- Only the owner is allowed to approve the certificate.
- Certificate is considered invalid if the issuer does not finalize the verification process..
- Optional - Only the owner can share his or her certificate to other people. (the idea behind this rule is that you do not want anyone to see your certificate’s information without permission incidentally).
Initializing Certificate Contract
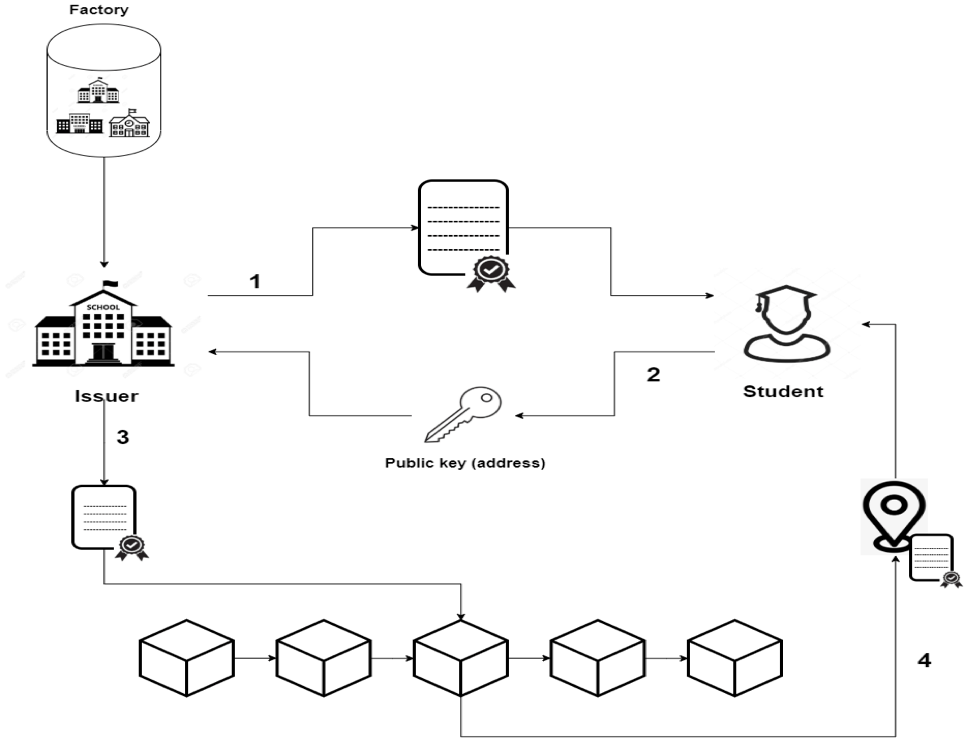
1. The issuer sends the certificate’s information to the owner.
2. The owner checks the information. If it is accurate, the owner then approves it by sending back his address (a unique identifier, usually a public key or derived from public key) to the issuer.
3. The issuer puts the owner address in the contract and deploys it to the blockchain network. The deployment of a contract is essentially sending a transaction containing the contract “bytecode”, and it is called contract creation transaction.
4. Once the transaction is included in blockchain, the issuer takes the address of that contract and sends it to the owner.
Optional – (2-step confirmation):

5. The owner once again approves the certificate to make sure there was not any mistake while passing the data to the certificate contract.
6. Only when the certificate was approved, the issuer then can finalize the verification.
In Step 5, if the certificate contains wrong information, I think it is a good idea to redeploy the contract rather than adding an extra function that allows the issuer to modify the information.
Related: Strategic Business Value of Blockchain in Insurance
Validating and Sharing Certificate Contract:
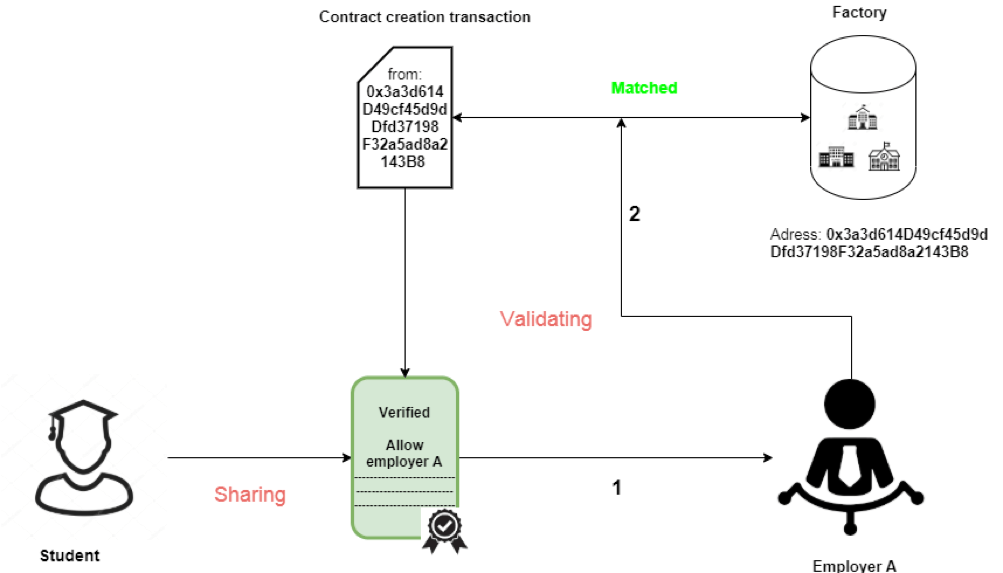
Sharing: The owner gives the employer his/her certificate address and permission to access the information.
Validating: The employer should go through 2 following steps to make sure the certificate is 100% authentic.
1. Check whether the certificate is verified.
2. Check the contract creation transaction of that certificate to see where it is made from. If the contract creator’s address is equal to the Factory’s address, it is authentic, and vice versa.
Of course, in the real-world application, no one wants to do step 2 manually, it may take quite a bit of time to do so. This is just a detailed explanation of how a Smart certificate works behind the scenes.
In conclusion, It is undeniable that blockchain does have a huge and positive influence on education and Smart certificate is just one in many other use cases that it provides to tackle educational challenges. Hopefully, someday, this special type of certificate will become more popular and replace the role of the traditional one.
Reference
- [1] (2015). “A Rising Tide of Bogus Degrees.” The New York Times. Accessed October 19, 2019. [Link]
- [2] Grasz, J. (2014). “Fifty-eight Percent of Employers Have Caught a Lie on a Resume, According to a New CareerBuilder Survey”. Accessed October 19, 2019. [Link
- [3] (2018). “University College London Becomes First UK Institution to Leverage Bitcoin Blockchain for Verification of Academic Qualifications”. Accessed October 10, 2019. [Link]
- [4] (2017). “University of Nicosia is the First University in the World to Publish Diplomas of All Graduating Students on the Blockchain”, Accessed October 10, 2019. [Link]
- [5] Redman J. (2016). “MIT Media Lab uses the bitcoin blockchain for digital certificates”. Accessed October 20, 2019. [Link]
- [6] (2016). “Sony Global Education Develops Technology Using Blockchain for Open Sharing of Academic Proficiency and Progress Records”. Accessed at October 20, 2019. [Link]
- [7] Imran Bashir (2017). Mastering Blockchain. Birmingham, UK: Packt Publishing Ltd.
- [8] Bartolomé, A., & Torlà, C., & Castañeda, L., & Adell, J. (2017). “Blockchain in education: Introduction and critical review of the state of the art”. 61. 10.21556/edutec.2017.61.
- [9] Chen, G., Xu, B., Lu, M., & Chen, N.-S. (2018). “Exploring blockchain technology and its potential applications for education. Smart Learning Environments”, 5(1). doi:10.1186/s40561-017-0050-x