The future of healthcare is digital, and the ongoing pandemic undoubtedly accelerates the transition. According to HIMSS, 80% of health systems plan to increase their investment in digital health in the next 5 years, with 58% of whom spending at least US$ 10 million annually by 2026. This trend is proven true for both clinicians and patients, with 75% and 50% of those surveyed supporting the use of digital health tools, respectively [1]. Here are the three technologies that help shape the healthcare of tomorrow.
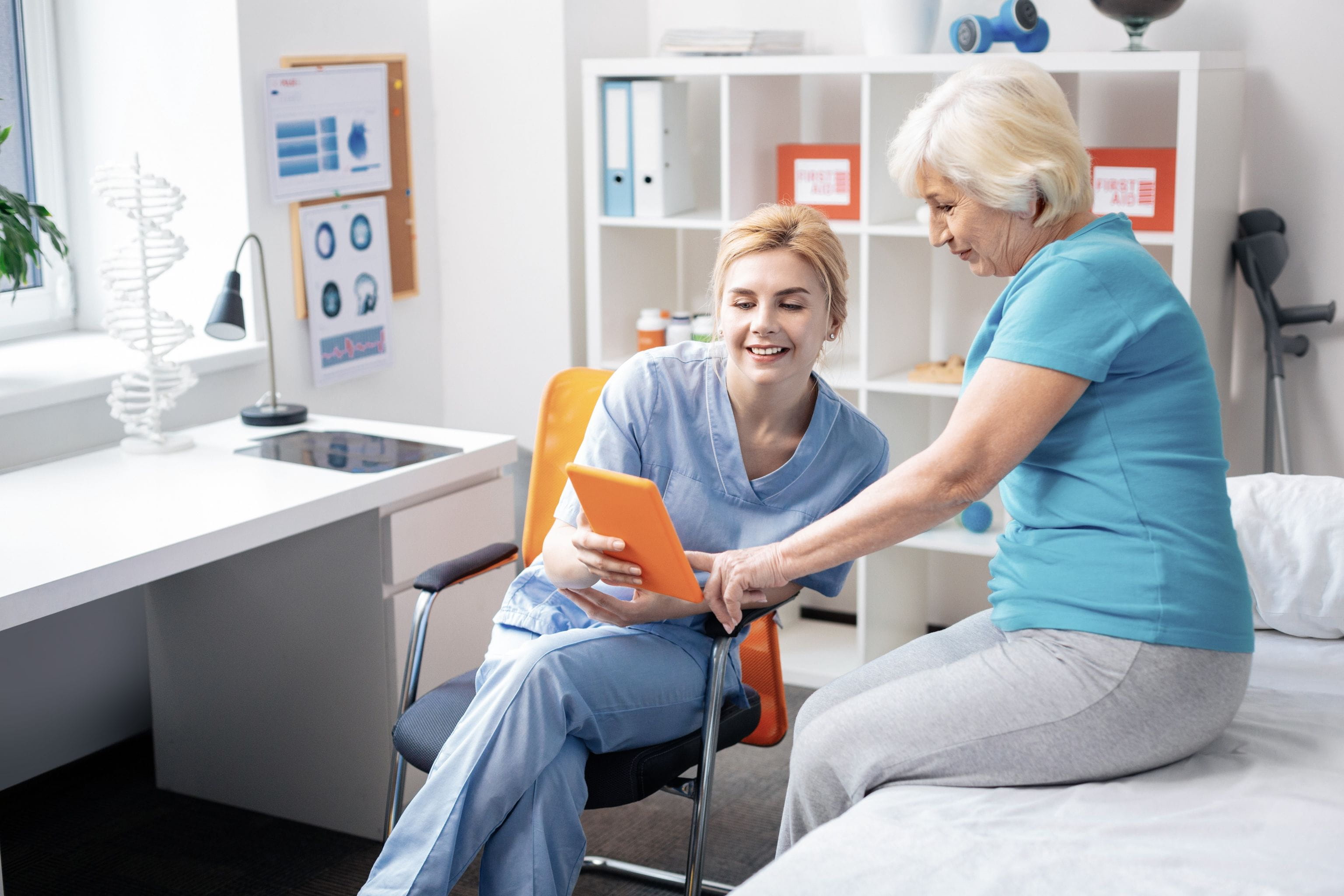
Virtual Healthcare
McKinsey estimates the current adoption rate of telehealth to be 38 times higher than the pre-pandemic level. What is more, up to US$ 250 million worth of healthcare services can be virtualized. The public’s favorable attitude towards remote healthcare largely contributes to such an optimistic estimation. 40% of the respondents plan to continue using virtual services even after the pandemic is over. Moreover, up to 60% of the surveyed are interested in a mixed plan of virtual services, including less expensive virtual-first healthcare [2]. Virtual healthcare undoubtedly remains a strategic priority for medical institutions. Indeed, investment in telemedicine reached US$ 4.3 billion in 2021 and was 139% higher than that of 2019 [3].
Benefits of virtual healthcare are unquestionable. For the provider side, telehealth helps free up capacity and protect hospitals from a sudden surge in demand. The UK National Health Service (NHS) recently utilizes telemedicine to cope with rising COVID cases caused by the Omicron variant. Under the “virtual wards” system, patients are remotely monitored and treated using monitoring apps, wearables and devices such as pulse oximeters. Data generated from these devices will be sent and analyzed by medical staff, and advice will be given accordingly. With further expansion, the NHS plans to treat 15% of COVID patients with this “virtual wards” system [4]. Post-COVID, virtual healthcare will continue to prove helpful with potential shortage of staffs and ageing populations. In the US alone, the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) predicts a 37,000 - 124,000 shortfall of physicians by 2034 [5]. Investing in telehealth is one way to mitigate the talent crunch crisis.
Artificial Intelligence
AI has recently emerged as the game-changer for the healthcare industry. It is estimated that the AI in healthcare market will grow from US$6.9 billion in 2021 to US$67.4 billion by 2027 [6]. The impact of AI in healthcare is broad and wide, benefiting both back-office operations and clinical activities such as diagnosis and care delivery. One area where AI has benefited significantly is diagnostics. In fact, AI applications have long been praised for improving diagnostic accuracy and opening new doors that were previously closed to human-based solutions. Take the collaboration between the NHS and HeartFlow as an example. Partnered for the better, the NHS has employed HeartFlow’s AI technology to assist diagnosis of coronary heart disease. The AI platform uses data from a patient’s CTA scan and creates a personalized, digital 3D model of the patient’s heart. It then uses an advanced algorithm to simulate the blood flow and how blockages might impact the patient’s coronary arteries. Prior to the technology, diagnosis of the heart disease was performed using a highly invasive and time-consuming technique called coronary angiography, which involves inserting a long, thin tube into the patient’s vessel and injecting a special type of dye. Such application of AI allows Newcastle Hospital to offer the CTA-first approach to more patients than previously (45% compared to 28%) [7]. This in turn reduces the patients’ risks and time spent at the clinic, which then translates into cost-saving for the hospital. When scaled across the NHS, HeartFlow’s AI platform is predicted to save £9.1 million annually for the UK health system [8].
Interested in exploring AI applications in healthcare from other stakeholders’ perspectives? Check out this article here.
Data Analytics
Thanks to technology, healthcare data is now widely available. Both traditional data from medical records, scans and prescriptions and new information extracted from wearables, smart devices and even social media can be effectively used in the healthcare sector. In fact, healthcare data was estimated to reach 4 trillion gigabytes in 2013, with projections that the number would be 10 times higher by now. What is more, approximately 80% of this data is unstructured [9]. So, making sense of this crazy large pool of data requires effective data analytics, which, when coupled with next-gen technology such as machine learning (a subfield of AI), would yield meaningful impacts. For example, Stevens Institute of Technology utilized AI to forecast future flu outbreaks 15 weeks in advance with an 11% increase in accuracy rate. Using machine learning, the organization was able to find hidden patterns by exploring the interaction between time and place, which allows them to make more precise forecasts than other methods [10]. Similarly, machine learning was utilized to predict suicide attempts in as little time as 7 days before. These predictions yield significantly higher accuracy rate than traditional methods. It is because conventional forecast tools can only study risk factors in isolation, whereas machine learning can analyze hundreds of factors together [11]. Although these studies are only in the research phase, such positive results signal a bright future for scalable application of data analytics in healthcare.
A digital transformation marathon
The healthcare sector might be a laggard in the digital transformation (DX) race pre-COVID, but the pandemic has brought DX to the forefront of corporate strategy. According to Accenture, medical organizations are compressing decades’ worth of DX effort into a 2 – 3 year timeline, with 93% of the respondents accelerating innovations with a sense of urgency [12]. Despite the pressure, medical institutions need to keep in mind that successful DX implementation requires more than just technology adoption. Having a clear DX roadmap, measurable ROI targets, comprehensive change management and an experienced partner to lean on are keys to winning the DX marathon.
What makes up successful digital transformation implementation? Check out this article here.
Sources:
[1] HIMSS. 2021 Future of Healthcare Report.
[2] McKinsey & Company. Telehealth: A quarter-trillion-dollar post-COVID-19 reality?
[3] PwC. Global Top Health Industry Issues 2021.
[4] The Times. Covid patients treated at home to protect NHS.
[5] AMMC. AAMC Report Reinforces Mounting Physician Shortage.
[6] Markets and Markets. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Market.
[7] Med Tech Innovations. NHS mandates AI-powered analysis to treat coronary heart disease.
[8] Medical Device Network. NHS adopts HeartFlow’s AI technology to tackle coronary heart disease.
[10] Stevens Institute of Technology. A.I. Tool Provides More Accurate Flu Forecasts.
[11] SAGE. Predicting Risk of Suicide Attempts Over Time Through Machine Learning.
[12] Accenture. Accenture Digital Health Technology Vision 2021.